Relevant Information Retrieval
In the realm of modern AI-powered assistants, a pivotal task is the retrieval of pertinent information. This process involves identifying and extracting the relevant segments of documents in response to a user's query, which are then processed by a large language model to formulate a response. The completeness of the extracted information directly influences the quality and comprehensiveness of the chatbot's answer. However, the presence of extraneous information can detract from the answer's quality, leading to a higher likelihood of inaccuracies or "hallucinations" — responses not grounded in the provided documents but generated from the model's general knowledge. Moreover, an overload of information can escalate the processing costs and time for handling the request.
The overall effectiveness of the search is assessed based on several criteria:
- The comprehensiveness of the answer and its ability to capture all nuances.
- The frequency of hallucinations, where the model responds with generalities not supported by the documents.
- The cost associated with processing the request.
- The speed at which the request is processed.
The Varex platform integrates a curated and optimized array of state-of-the-art information retrieval (IR) technologies. This setup enables users to tailor the system according to their specific needs and priorities.
Retriever Types
1. Simple Embeddings Similarity Search
This method is widely favored for its simplicity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. It involves segmenting the text into chunks, computing vectors that encapsulate the semantic essence of each chunk, and identifying the most relevant text segments for a given query. There are numerous embedding models available, offering varying degrees of search precision across different data types and domains. Varex provides access to the most advanced models currently available, with many of these models performing optimally in English compared to other languages.
Settings:
embed_model: Specifies the embedding model to be used. Available options include:openai_multilingual: OpenAI's multilingual model.cohere_en: Cohere's model for English only.cohere_multilang: Cohere's multilingual model.mistral_multilingual: Mistral's multilingual model.gemini_multilingual: Gemini's multilingual model.voyage_en: Voyage's model for English only.voyage_multilang: Voyage's multilingual model.jina_en: Jina's model for English only.together_en: Together's model for English only.
2. Hybrid Search
This is the recommended search model, combining various approaches to enhance search quality significantly over simple embeddings similarity search. This model is particularly effective in handling specialized terminology, spelling errors, and product names. It employs a sophisticated mix of embeddings similarity search, full-text search, and grammatical error correction, among other techniques.
Additional settings and options for this search type can greatly impact accuracy, costs, and response times. Optionally, after the search phase, responses can be further sorted to improve accuracy and completeness, albeit at the expense of increased response times and costs.
Settings:
embed_model: Specifies the embedding model to be used. Same options as above.use_basic_reranker: Determines whether a basic fast reranker should be employed to enhance search outcomes. This is currently not recommended for non-English languages or without translating to English.use_llm_reranker: Considers the use of an advanced LLM reranker for further refinement of search results following the base reranker. While this option increases costs and response times, it significantly enhances effectiveness.compress_results: A boolean setting indicating whether to apply a prompt compression technique with a cost-effective LLM, potentially lowering costs and improving answer quality for queries requiring extensive source text (e.g., detailed product descriptions) or information from large datasets. This setting may lengthen response times and is less beneficial for straightforward Q&A scenarios. See: LLMLingua: Innovating LLM Efficiency with Prompt Compression (opens in a new tab)
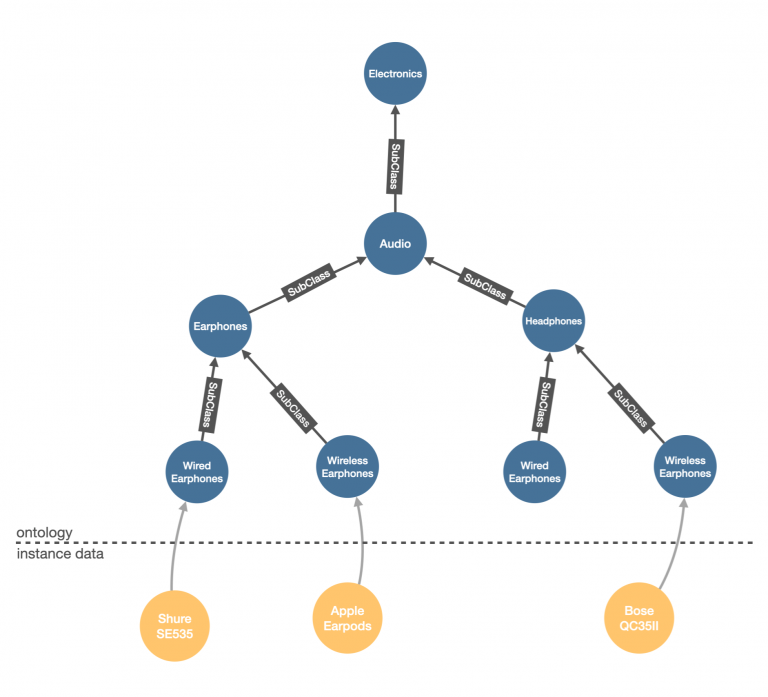
Knowledge Graph Basic Search
The Knowledge Graph Basic Search employs a structured approach to information organization, utilizing a hierarchical tree model. This method starts with broad categories at the apex of the hierarchy and progressively narrows down to more specific levels, akin to organizing a vast collection of books by dividing them into sections, shelves, and eventually individual titles. To locate a specific piece of information—or "book"—users start at the general category and sequentially refine their search through subcategories, thereby streamlining the path to the desired information. This methodical division of options into smaller, more manageable segments at each step aims to facilitate an efficient and directed search process.
This search mechanism represents the pinnacle of sophistication in the tools developed and maintained by the Varex team. It is renowned for delivering the most precise outcomes and is particularly effective in minimizing inaccuracies or "hallucinations" that can occur with other search methods. However, its reliance on large language models (LLMs) as the underlying technology incurs higher costs and longer execution times. This trade-off underscores its use as a high-accuracy, high-fidelity search solution for those who prioritize precision and reliability in their information retrieval needs.